Coughing is a common reflex action that helps clear the airways of mucus, irritants, or foreign particles. While occasional coughing is normal and beneficial, persistent or severe coughing can indicate an underlying health issue. This guide provides an overview of the types, causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of coughs.
Types of Coughs:
- Acute Cough: Lasts for less than three weeks and is often associated with viral respiratory infections, such as the common cold or flu.
- Subacute Cough: Persists for three to eight weeks and may be a lingering symptom of a previous respiratory infection.
- Chronic Cough: Lasts for eight weeks or longer and may indicate an underlying medical condition, such as asthma, allergies, gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), or chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD).
Coughs can be categorized based on their sound and duration:
- Dry cough: This non-productive cough has no mucus and can be irritating and persistent.
- Wet cough: This productive cough produces mucus and is often associated with infections or allergies.
- Hacking cough: This harsh, forceful cough can be caused by irritation or inflammation.
- Barking cough: This cough sounds similar to a dog’s bark and is often associated with croup in children.
- Whooping cough: This characteristic cough has a high-pitched “whoop” sound and requires medical attention.
Causes of Coughs:
- Viral Respiratory Infections: Including the common cold, influenza (flu), bronchitis, and pneumonia.
- Allergies: Exposure to allergens such as pollen, dust, pet dander, or mold can trigger coughing.
- Environmental Irritants: Cigarette smoke, air pollution, strong odors, and chemical fumes can irritate the airways and lead to coughing.
- Chronic Respiratory Conditions: Such as asthma, COPD, bronchiectasis, or interstitial lung disease.
- Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD): Acid reflux can cause irritation of the esophagus and lead to a persistent cough.
- Medications: Certain medications, such as angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors used to treat high blood pressure, can cause a chronic cough as a side effect.
- Postnasal Drip: Excess mucus dripping down the back of the throat can trigger coughing.
- Smoking: Both active smoking and exposure to secondhand smoke can irritate the airways and lead to coughing.
Symptoms of Coughs:
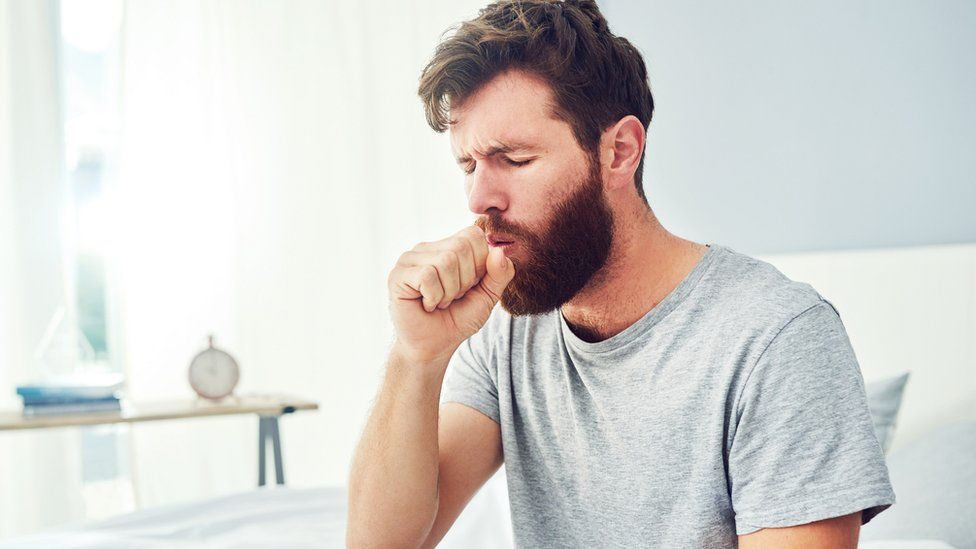

- Dry or productive cough (producing mucus or phlegm)
- Sore throat or throat irritation
- Hoarseness or voice changes
- Wheezing or difficulty breathing
- Chest pain or discomfort
- Fatigue or weakness
- Fever (in cases of viral respiratory infections)
Diagnosis of Coughs:
Your healthcare provider will perform a thorough medical history assessment and physical examination to determine the underlying cause of your cough. Diagnostic tests may include:
- Chest X-ray: To evaluate the lungs and airways for signs of infection, inflammation, or structural abnormalities.
- Pulmonary Function Tests: To assess lung function and rule out conditions such as asthma or COPD.
- Sputum Culture: To identify the presence of bacteria or fungi in respiratory secretions.
- Allergy Testing: To identify specific allergens that may be triggering your cough.
- Esophageal pH Monitoring: To evaluate for gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) if indicated.
What causes a cough?
Coughs are a natural reflex triggered by irritation in your airways. This irritation can be caused by various factors, including:
- Infections: Viral or bacterial infections of the upper respiratory tract (common cold, flu, bronchitis) are the most common causes.
- Allergies: Dust, pollen, pet dander, and other allergens can irritate your airways, leading to coughing.
- Asthma: This chronic condition causes inflammation and narrowing of the airways, leading to coughing, wheezing, and shortness of breath.
- Irritants: Smoke, dust, pollution, and fumes can irritate your airways and trigger coughing.
- Medications: Certain medications, like ACE inhibitors used for blood pressure, can cause a dry cough as a side effect.
- Acid reflux (GERD): Stomach acid refluxing up into your esophagus can irritate your airways and trigger a cough, especially at night.
- Postnasal drip: Excess mucus dripping down the back of your throat can irritate your airways and cause coughing.
How do I know if my cough is serious?
While most coughs are harmless and resolve on their own within a few weeks, some require medical attention. Here are some signs that your cough might be serious:
- Coughing for more than 3 weeks: A persistent cough, especially if it worsens or doesn’t improve, could indicate an underlying condition.
- Fever: A high fever (over 100.4°F) accompanying your cough could signify a more serious infection.
- Wheezing: Difficulty breathing or wheezing with your cough could indicate asthma or other respiratory problems.
- Blood in your mucus: Coughing up blood is always a cause for concern and requires immediate medical attention.
- Shortness of breath: If you experience difficulty breathing or shortness of breath with your cough, seek medical attention promptly.
Remember: This information is for general understanding and not a substitute for professional medical advice. If you are concerned about your cough or experience any of the serious symptoms mentioned above, consult a doctor for proper diagnosis and treatment.
Treatment of Coughs:
Treatment for coughs depends on the underlying cause and may include:
- Over-the-Counter Medications: Such as cough suppressants (dextromethorphan), expectorants (guaifenesin), antihistamines (for allergies), or decongestants (for nasal congestion).
- Prescription Medications: Such as bronchodilators or inhaled corticosteroids for asthma, proton pump inhibitors for GERD, or antibiotics for bacterial infections.
- Home Remedies: Including staying hydrated, using a humidifier, gargling with salt water, sucking on throat lozenges or hard candies, and consuming honey or herbal teas.
- Lifestyle Modifications: Quitting smoking, avoiding exposure to environmental irritants, maintaining a healthy diet and weight, and practicing good hygiene to prevent the spread of respiratory infections.
Prevention of Coughs:
- Practice good hand hygiene by washing your hands frequently with soap and water, especially during cold and flu season.
- Avoid close contact with individuals who have respiratory infections.
- Get vaccinated against influenza (flu) and pneumonia as recommended by your healthcare provider.
- Keep your immune system strong by eating a balanced diet, getting regular exercise, managing stress, and getting enough sleep.
When to See a Healthcare Provider:
Seek medical attention if your cough:
- Persists for more than three weeks or is severe and disruptive.
- Is accompanied by difficulty breathing, chest pain, wheezing, or coughing up blood.
- Is associated with high fever, chills, night sweats, or unintended weight loss.
- Is accompanied by other concerning symptoms or is impacting your quality of life.
In conclusion, while coughing is often a normal and necessary bodily reflex, persistent or severe coughing may indicate an underlying health issue that requires medical attention. By understanding the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of coughs, you can better manage your respiratory health and seek appropriate care when needed. Always consult your healthcare provider for personalized advice and treatment recommendations based on your specific condition and medical history.